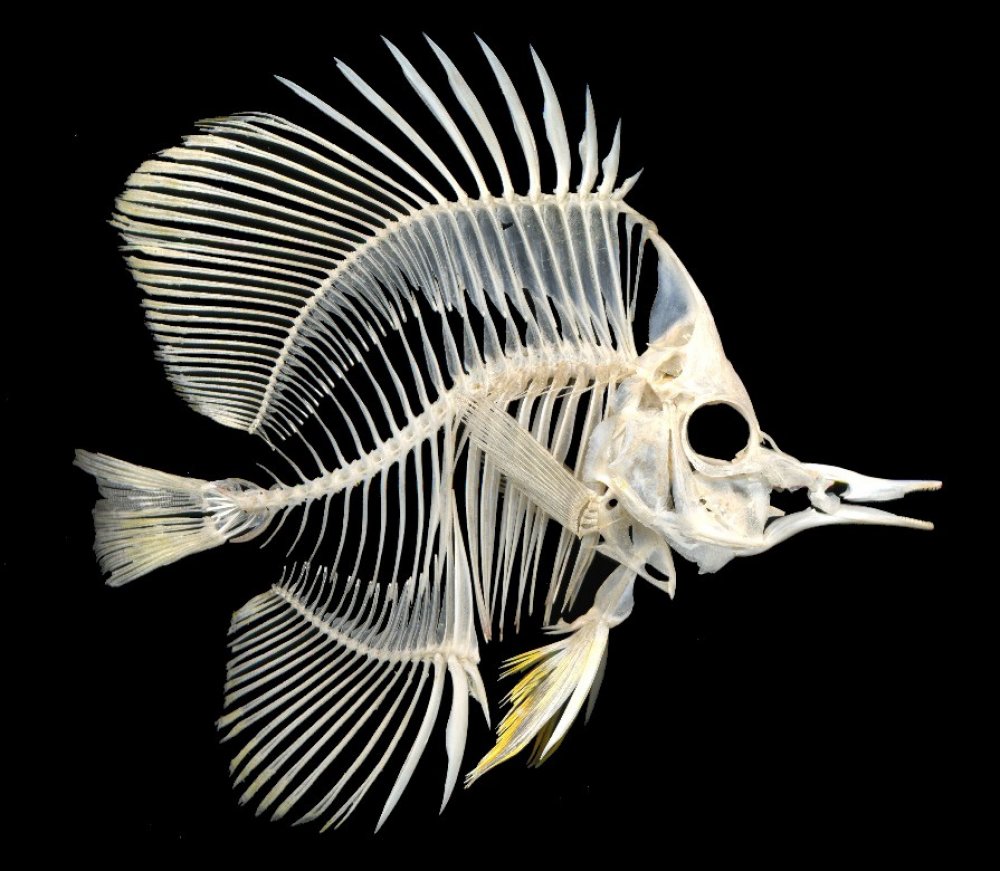

Introduction
When we think of fish, we often imagine their vibrant colors and graceful movements underwater. However, beyond their beauty lies an intricate skeletal structure that supports their bodies and allows them to swim effortlessly. In this article, we will delve into the world of fish skeletons, exploring their composition, functions, and the fascinating insights they provide into aquatic life.
The Composition of a Fish Skeleton
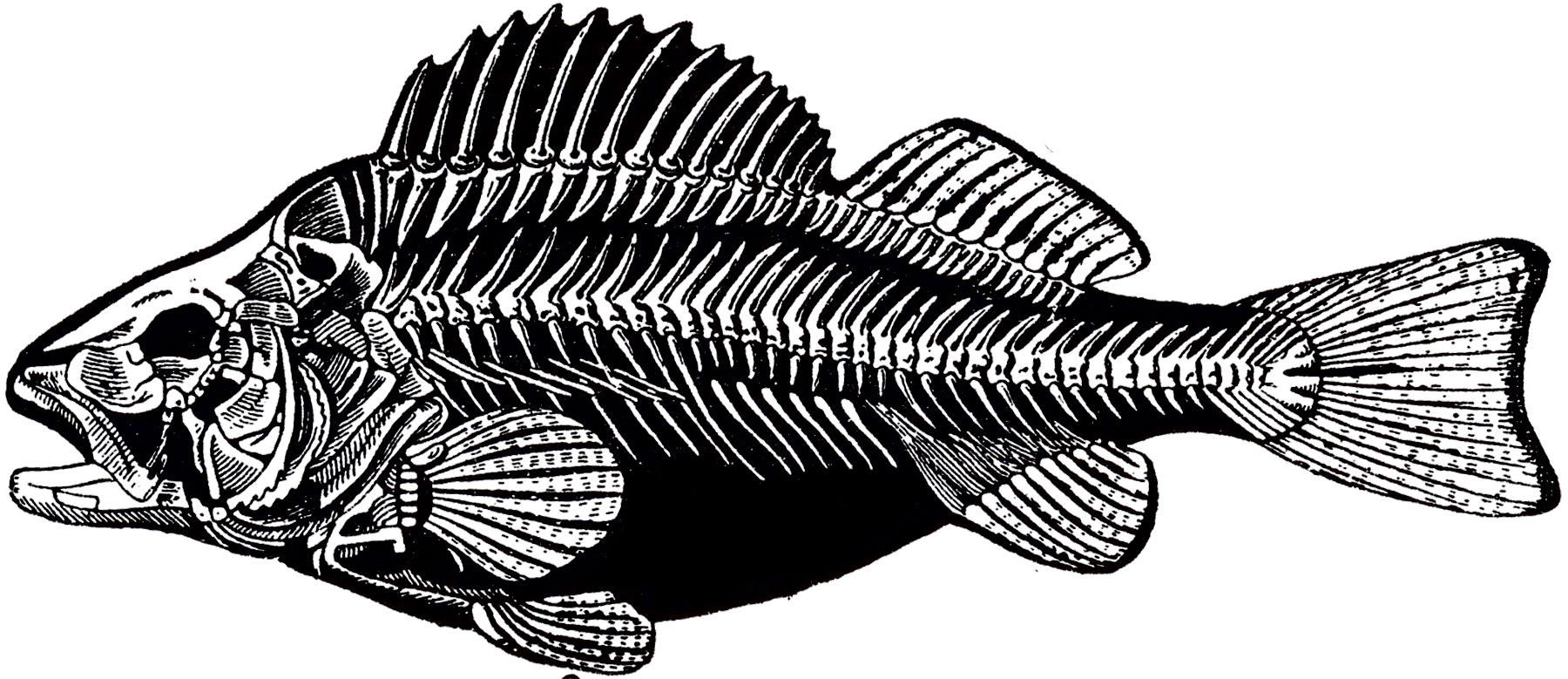
A fish skeleton comprises various bones and cartilages that work together harmoniously. The main components of a fish's skeletal system include the skull, vertebral column, fins, and ribs. These structures are made up of calcium, phosphorus, and collagen, providing strength and flexibility to the overall framework of the fish.
The Skull: Protecting Vital Organs

The skull of a fish serves a crucial role in protecting its delicate brain and sensory organs. Unlike mammals, fish have a relatively simplified skull structure. It consists of several bones that encase the brain and house the eyes, nostrils, and inner ear. The shape and size of the skull can vary significantly among different fish species, reflecting their unique adaptations and ecological niches.
The Vertebral Column: Providing Flexibility
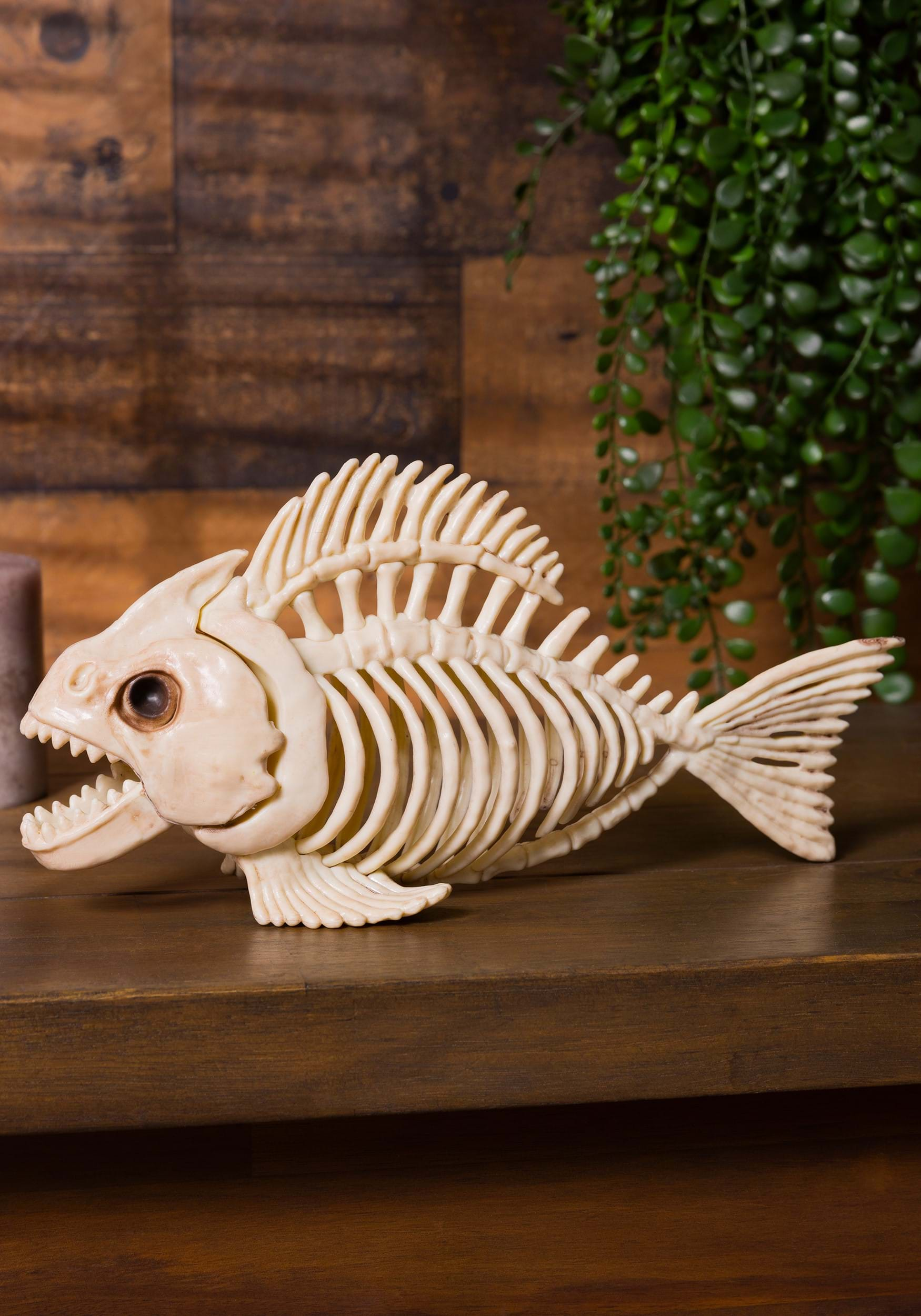

One of the most distinct features of a fish skeleton is its vertebral column, also known as the backbone. Composed of a series of small bones called vertebrae, the vertebral column provides flexibility and support to the fish's body. It allows the fish to bend, twist, and swim with remarkable agility. Additionally, the vertebral column plays a crucial role in protecting the fish's spinal cord, a vital component of its nervous system.
Fins: Enhancing Maneuverability
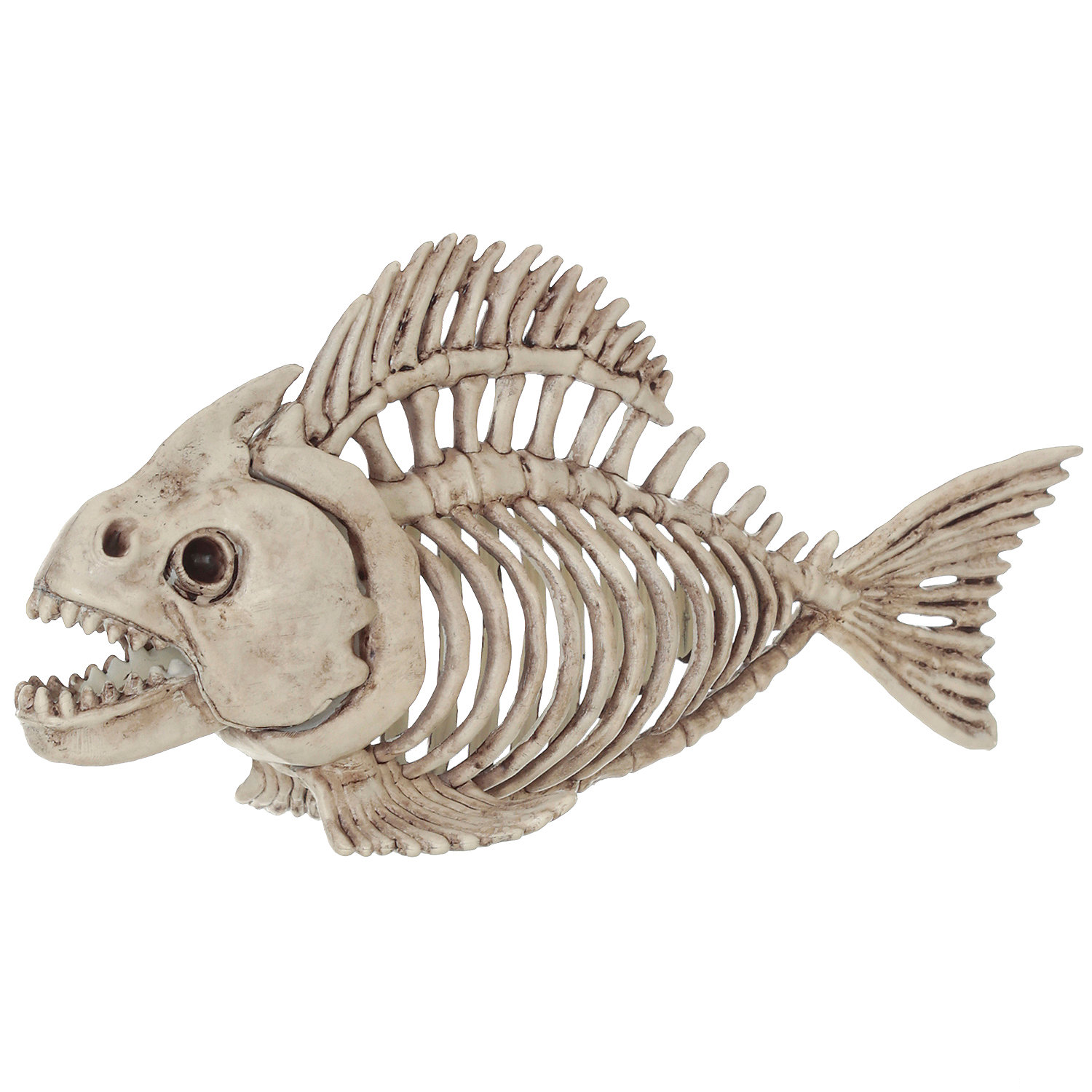

Fish rely on their fins for balance, stability, and precise movements in water. The fins are supported by rays or spines connected to the fish's skeletal structure. Each type of fin, including the dorsal fin, caudal fin, pectoral fin, pelvic fin, and anal fin, serves a specific purpose. Whether it's propelling forward, changing direction, or maintaining stability, the fins contribute significantly to a fish's maneuverability.
Ribs: Protecting Internal Organs
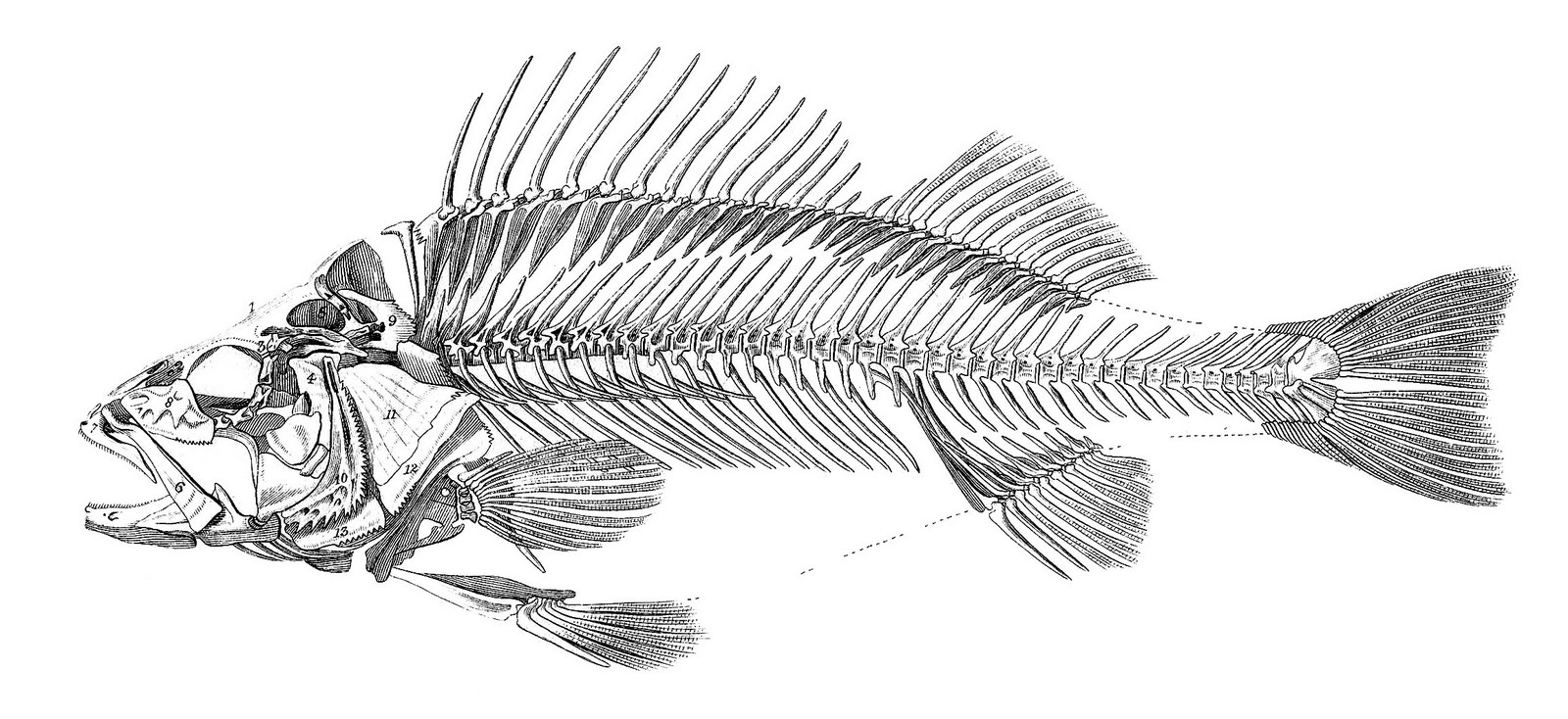
Similar to other vertebrates, fish possess ribs that surround and protect their internal organs, such as the heart and liver. However, fish ribs differ from those of mammals in that they are not directly connected to the sternum or breastbone. Instead, fish ribs are primarily attached to the vertebral column, providing additional support and stability to the fish's body.
Adaptations and Diversity in Fish Skeletons
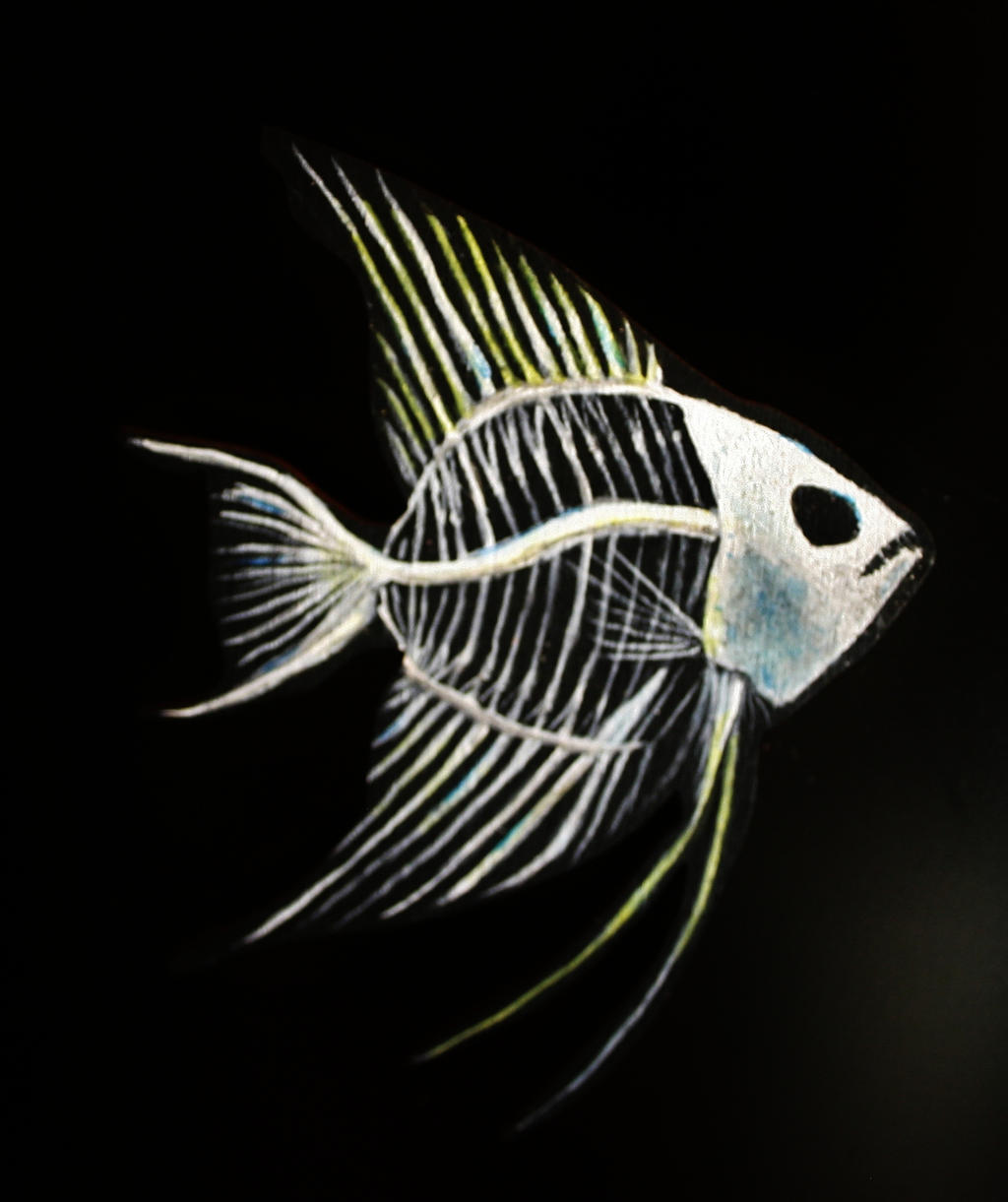

The skeletal structure of fish exhibits an incredible diversity, with adaptations tailored to their specific environments and lifestyles. Fish species inhabiting different habitats, such as freshwater, saltwater, deep-sea, or coral reefs, have distinct skeletal features that enable them to thrive in their respective ecosystems. From the elongated bodies of eels to the flattened skeletons of rays, each adaptation serves a unique purpose and reflects the remarkable adaptability of fish.
Fish Skeletons as Ecological Indicators

Beyond their anatomical significance, fish skeletons play a crucial role in ecological studies. The examination of fish remains, including skeletons, can provide valuable insights into the health of aquatic ecosystems. By analyzing the abundance, diversity, and condition of fish skeletons, researchers can assess the impact of environmental factors, such as pollution or climate change, on fish populations and their habitats.
Preservation and Fossilization of Fish Skeletons
Fish skeletons have the potential to be preserved as fossils under specific conditions. Fossilized fish skeletons have provided scientists with invaluable information about the evolution and history of fish. Through careful examination of fossilized bones, scientists can uncover details about the morphology, behavior, and ecological interactions of ancient fish species, contributing to our understanding of past ecosystems and the development of life on Earth.
In Conclusion
From their intricate composition to their remarkable adaptations, fish skeletons offer a window into the world beneath the water's surface. These skeletons not only provide structural support for fish but also serve as valuable tools for scientists studying aquatic ecosystems and the history of life on Earth. By unraveling the secrets hidden within fish skeletons, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and complexity of the natural world.